 From this
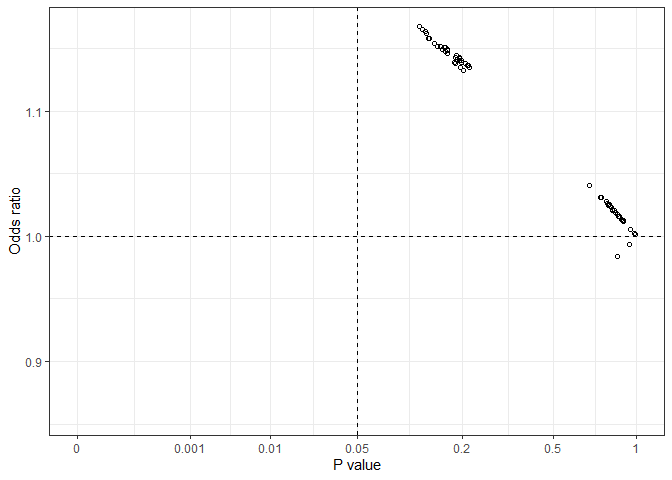
From this all_plot graph, we can see that all estimated odds ratio values fell in the left-side two quarters, with either a positive or a negative association but p values in all possible models were greater than 0.05.Calculates effect estimates from models with all possible combinations of a list of variables specified by users. Effect estimates can be regression coefficients, odds ratios and hazard ratios depending on modeling methods. This approach can be used for assessing treatment effects in clinical trials or the effects of a risk factor in observational biomedical and epidemiological studies.
You can install the released version of allestimates from CRAN with:
Using diab_df data to assess the association between marital status Married and and Diabetes as an example. Several other factors might potentially influence the association (odds ratio estimates) between Married and Diabetes variables.
library(allestimates)
data(diab_df)
diab_df$Overweight = as.numeric(diab_df$BMI >= 25)
vlist <- c("Age", "Sex", "Education","Smoke", "BMI", "Income")
results <- all_speedglm(crude = "Diabetes ~ Married", xlist = vlist, data = diab_df)
#> estimate: Odds Ratio or Rate Ratio
#> Crude model: Diabetes ~ MarriedAll those possible effect estimates (odds ratios in this case) are stored in an object results and can be used later for further analysis and generating various graphs.
 From this
From this all_plot graph, we can see that all estimated odds ratio values fell in the left-side two quarters, with either a positive or a negative association but p values in all possible models were greater than 0.05.
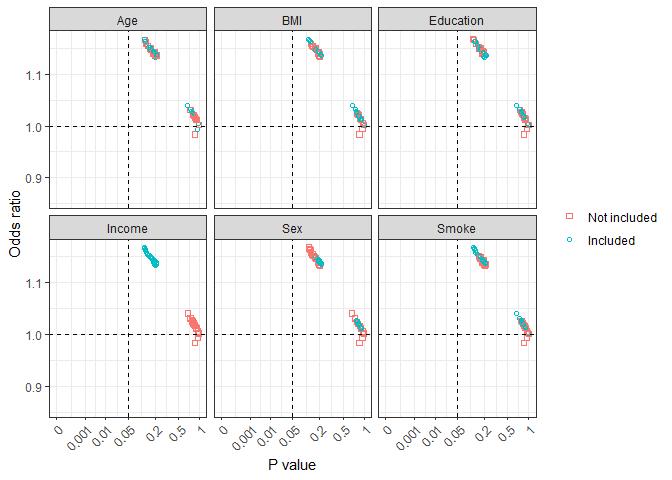
all_plot2 graph shows effect estimates with a specific variable being included or not included in the model. This can be helpful in combination with biological background knowledge to understand potential confounding effects, uncertainly of the effect estimates, and inappropriate inclusion of some variables.
Note: Interaction terms and other derived variables can be listed. Those terms need to be generated first before running an allestimates function.