extendedFamily adds new links to R’s generalized linear models. These families are drop in additions to existing families.
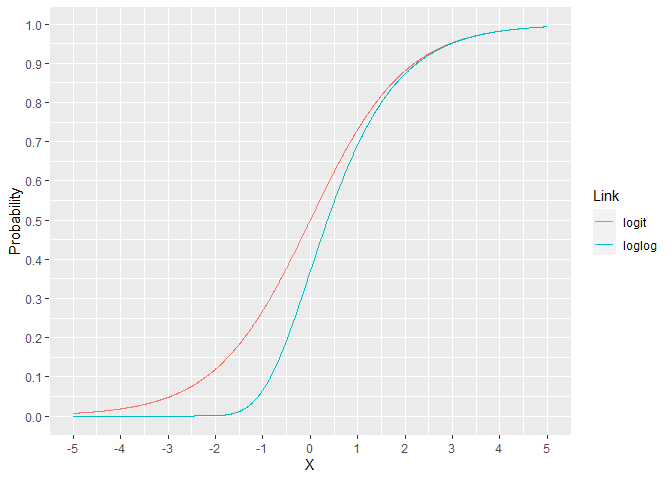
For the binomial family, the link is usually the logit but there are other options. The loglog model assigns a lower probability for X ranging from -5 to 2. For X over 2, the models are essentially indistinguishable. This can lead to improved performance when the response rate is much lower than 50%.
The heart data contains info on 4,483 heart attack victims. The goal is to predict if a patient died in the next 48 hours following a myocardial infarction. The low death rate makes this data set a good candidate for the loglog link.
Only the family object needs to change to use the loglog link.
glmLogit <- glm(formula = death ~ anterior + hcabg + kk2 + kk3 + kk4 + age2 + age3 + age4,
data = heart, family = binomial(link = "logit"))
glmLoglog <- glm(formula = death ~ anterior + hcabg + kk2 + kk3 + kk4 + age2 + age3 + age4,
data = heart, family = binomialEF(link = "loglog"))AUC improved by changing the link.
predictions <- heart %>%
select(death) %>%
mutate(death = factor(death, levels = c("1", "0")),
logitProb = predict(object = glmLogit, newdata = heart, type = "response"),
loglogProb = predict(object = glmLoglog, newdata = heart, type = "response"))
roc_auc(data = predictions, truth = death, logitProb)
#> # A tibble: 1 x 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 roc_auc binary 0.797
roc_auc(data = predictions, truth = death, loglogProb)
#> # A tibble: 1 x 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 roc_auc binary 0.801