This package aims to estimate Nonparametric Cumulative-Incidence Based Estimation of the Ratios of Sub-Hazard Ratios to Cause-Specific Hazard Ratios.
You can install the latest version of hrcomprisk in CRAN or the development version from Github:
# Install hrcomprisk from CRAN
install.packages("hrcomprisk")
# Or the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("AntiportaD/hrcomprisk")hrcomprsk packageYou can use the dataset provided by the authors from the CKiD study, wich has the necessary variables to run the package.
library(hrcomprisk)
data <- hrcomprisk::dat_ckid
dim(data) #dimensions
#> [1] 626 13
names(data) #variable names
#> [1] "b1nb0" "event" "male1fe0" "incomelt30" "incomegt75"
#> [6] "lps" "foodassist" "public" "matedultcoll" "privatemd"
#> [11] "entry" "exit" "inckd"The package will create a data.frame object with the cumulative incidence of each competing risk for each exposure group. We can use the CRCumInc fuction.
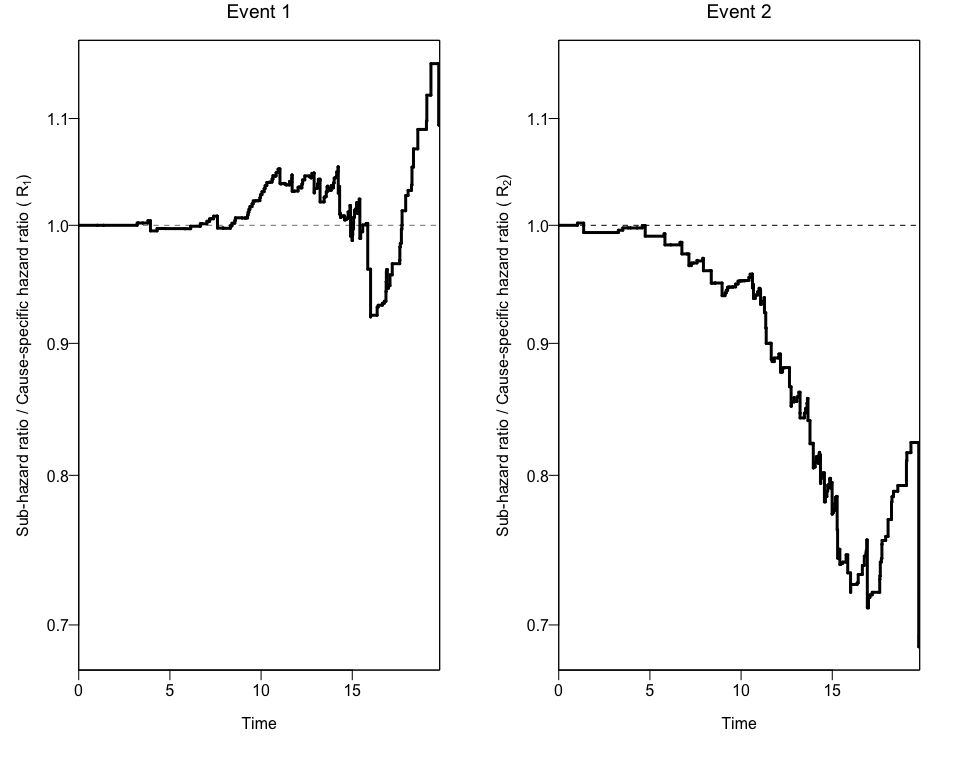
mydat.CIF<-CRCumInc(df=data, time=exit, event=event, exposed=b1nb0, print.attr=T)
#> $names
#> [1] "event" "exposure" "time" "CIoinc_comp" "CIxinc_comp"
#> [6] "CIoinc_1" "CIxinc_1" "CIoinc_2" "CIxinc_2" "R1"
#> [11] "R2"
#>
#> $class
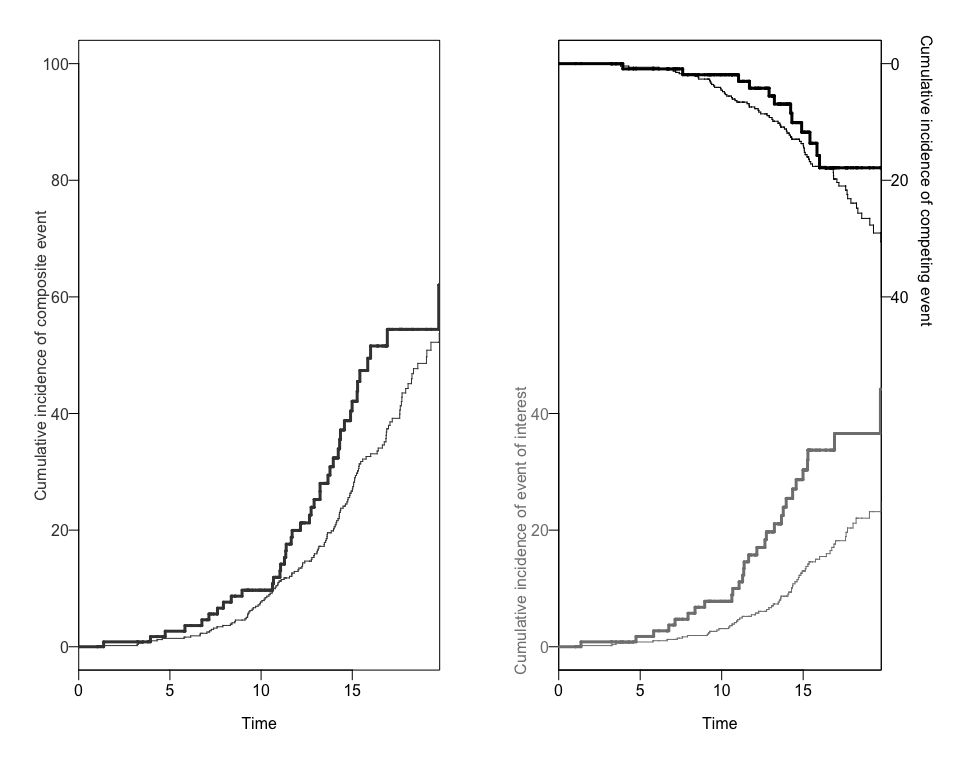
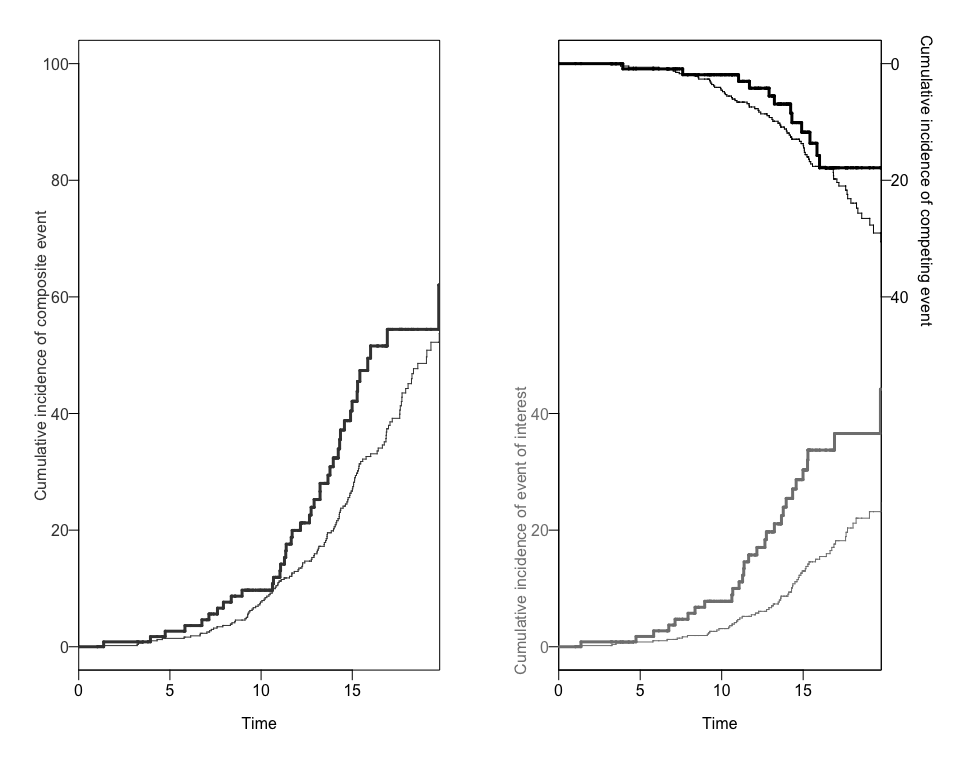
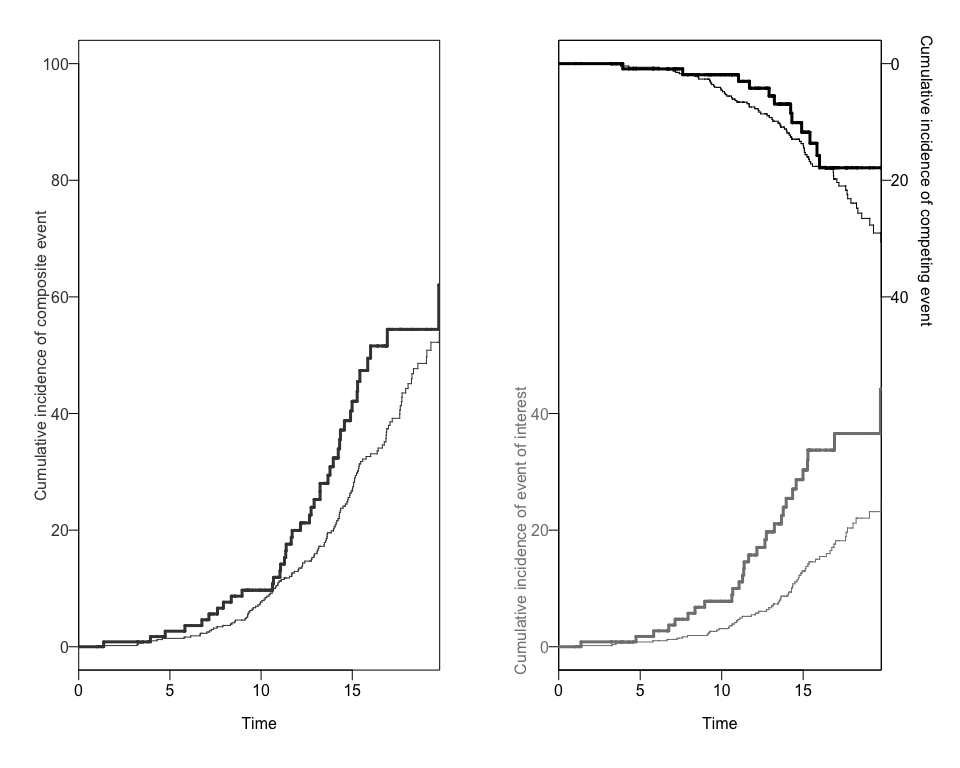
#> [1] "data.frame"We can also obtain two different plots using the plotCIF function:


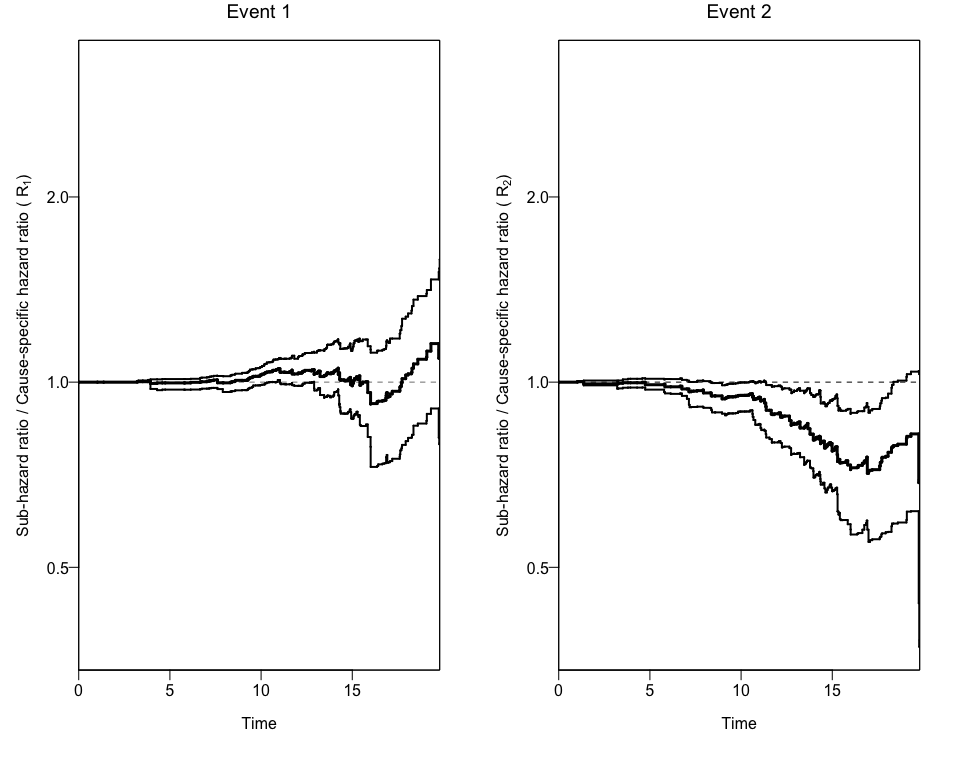
In order to get confidence intervals to the ratio of Hazard Ratios (Rk), we can use the bootCRCumInc function:
ciCIF<-bootCRCumInc(df=data, exit=exit, event=event, exposure=b1nb0, rep=100, print.attr=T)
#> $names
#> [1] "R1.lower" "R1.upper" "R2.lower" "R2.upper"
#>
#> $class
#> [1] "data.frame"Finally, we can use this new data to add the 95% Confidence Intervals to the previous plot using again the plotCIF function.
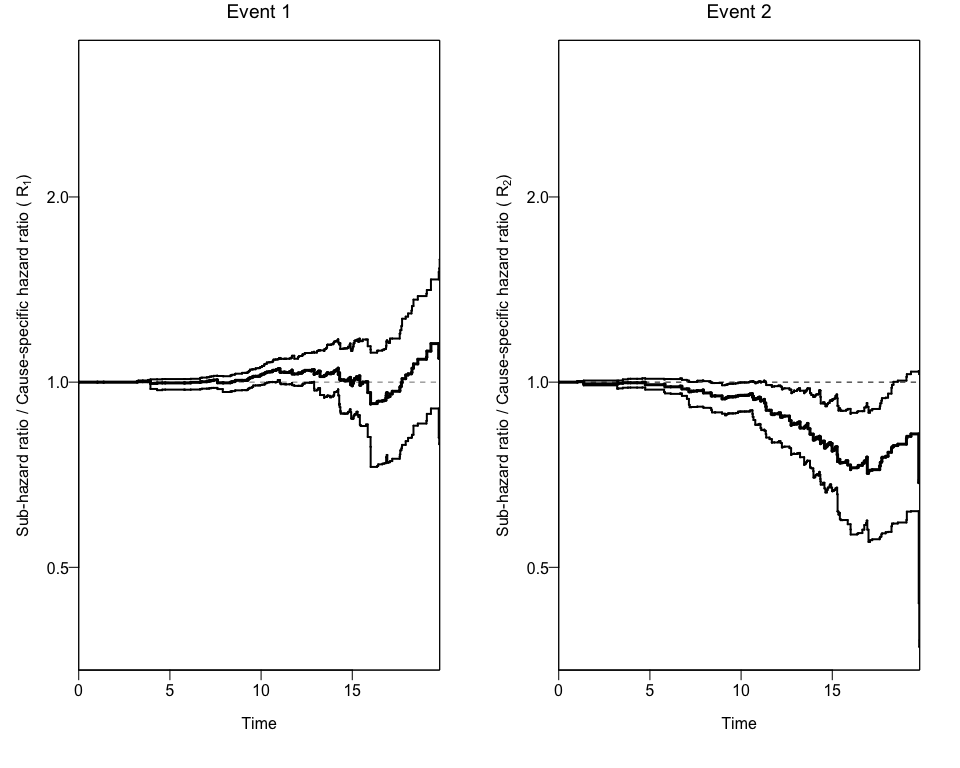
npcrestThe package also offers a wrapper function (npcrest) to do all these analyses in one step.
npcrest(df=data, exit=exit, event=event, exposure=b1nb0,rep=100, maxtime=20, print.attr=T)
#> $names
#> [1] "event" "exposure" "time" "CIoinc_comp" "CIxinc_comp"
#> [6] "CIoinc_1" "CIxinc_1" "CIoinc_2" "CIxinc_2" "R1"
#> [11] "R2"
#>
#> $class
#> [1] "data.frame"
#>
#> $names
#> [1] "R1.lower" "R1.upper" "R2.lower" "R2.upper"
#>
#> $class
#> [1] "data.frame"