NOTE An online openair book is being developed, see https://bookdown.org/david_carslaw/openair/.
For the main openair website, see https://davidcarslaw.github.io/openair/.
openair is an R package developed for the purpose of analysing air quality data — or more generally atmospheric composition data. The package is extensively used in academia, the public and private sectors. The project was initially funded by the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), with additional funds from Defra. The most up to date information on openair can be found in the package itself and at the book website here.
Further details, including blogs on openair can be found at davidcarslaw.com
Installation of openair from GitHub is easy using the devtools package. Note, because openair contains C++ code a compiler is also needed. For Windows - for example, Rtools is needed.
require(devtools)
install_github('davidcarslaw/openair')openair has developed over several years to help analyse atmospheric composition data; initially focused on air quality data.
This package continues to develop and input from other developers would be welcome. A summary of some of the features are:
importAURN and
importKCL functions.timeAverage
and selectByDate to make it easier to manipulate
atmospheric composition data.windRose and pollutionRose.type
option available in most functions.type
option to easily evaluate models by season, hour of the day etc. These
include key model statistics, Taylor Diagram, Conditional Quantile
plots.It is easy to import hourly data from 100s of sites and to import several sites at one time and several years of data.
library(openair)
kc1 <- importAURN(site = "kc1", year = 2011:2012)
kc1
## # A tibble: 17,544 × 18
## site code date co nox no2 no o3 so2 pm10
## <chr> <fct> <dttm> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 00:00:00 0.2 44 38 4 14 5 40
## 2 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 01:00:00 0.2 38 29 6 28 3 36
## 3 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 02:00:00 0.2 32 31 1 18 3 31
## 4 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 03:00:00 0.2 31 29 1 14 3 31
## 5 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 04:00:00 0.2 31 29 1 16 3 29
## 6 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 05:00:00 0.1 29 27 1 24 3 25
## 7 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 06:00:00 0.1 27 25 1 24 3 25
## 8 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 07:00:00 0.1 31 29 1 18 3 28
## 9 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 08:00:00 0.2 55 44 8 4 3 24
## 10 London N… KC1 2011-01-01 09:00:00 0.2 57 44 9 6 3 24
## # … with 17,534 more rows, and 8 more variables: pm2.5 <dbl>, v10 <dbl>,
## # v2.5 <dbl>, nv10 <dbl>, nv2.5 <dbl>, ws <dbl>, wd <dbl>, air_temp <dbl>Using the selectByDate function it is easy to select
quite complex time-based periods. For example, to select weekday (Monday
to Friday) data from June to September for 2012 and for the
hours 7am to 7pm inclusive:
sub <- selectByDate(kc1,
day = "weekday",
year = 2012,
month = 6:9,
hour = 7:19)
sub
## # A tibble: 1,118 × 18
## date site code co nox no2 no o3 so2 pm10
## <dttm> <chr> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2012-06-01 07:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 36 23 9 24 3 6
## 2 2012-06-01 08:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 33 21 7 34 3 9
## 3 2012-06-01 09:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 23 19 2 52 3 6
## 4 2012-06-01 10:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 17 13 2 62 3 7
## 5 2012-06-01 11:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 17 13 2 70 3 9
## 6 2012-06-01 12:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 21 19 1 78 3 8
## 7 2012-06-01 13:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 36 29 5 68 3 9
## 8 2012-06-01 14:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 25 21 2 80 3 6
## 9 2012-06-01 15:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 27 23 2 80 3 7
## 10 2012-06-01 16:00:00 London N… KC1 0.23 34 29 4 58 3 10
## # … with 1,108 more rows, and 8 more variables: pm2.5 <dbl>, v10 <dbl>,
## # v2.5 <dbl>, nv10 <dbl>, nv2.5 <dbl>, ws <dbl>, wd <dbl>, air_temp <dbl>Similarly it is easy to time-average data in many flexible ways. For example, 2-week means can be calculated as
sub2 <- timeAverage(kc1, avg.time = "2 week")type optionOne of the key aspects of openair is the use of the type
option, which is available for almost all openair functions. The
type option partitions data by different categories of
variable. There are many built-in options that type can
take based on splitting your data by different date values. A summary of
in-built values of type are:
hemisphere option that can be either
“northern” (default) or “southern”longitude and latitudewd) is available
type = "wd" will split the data up into 8 sectors: N, NE,
E, SE, S, SW, W, NW.type = "season" will just split the data into
four seasons regardless of the year.If a categorical variable is present in a data frame
e.g. site then that variables can be used directly
e.g. type = "site".
type can also be a numeric variable. In this case the
numeric variable is split up into 4 quantiles i.e. four
partitions containing equal numbers of points. Note the user can supply
the option n.levels to indicate how many quantiles to
use.
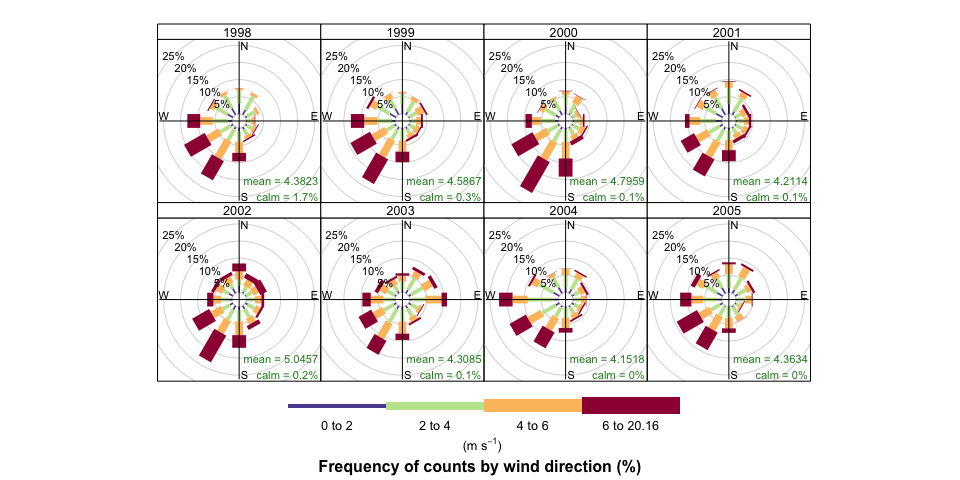
openair can plot basic wind roses very easily
provided the variables ws (wind speed) and wd
(wind direction) are available.
windRose(mydata)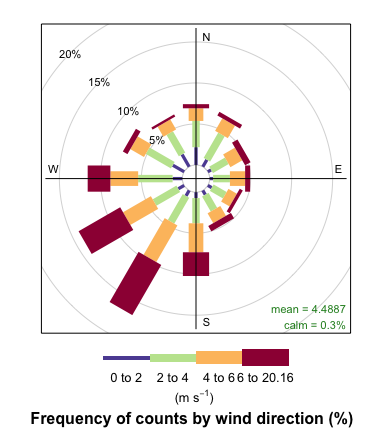
However, the real flexibility comes from being able to use the
type option.
windRose(mydata, type = "year", layout = c(4, 2))